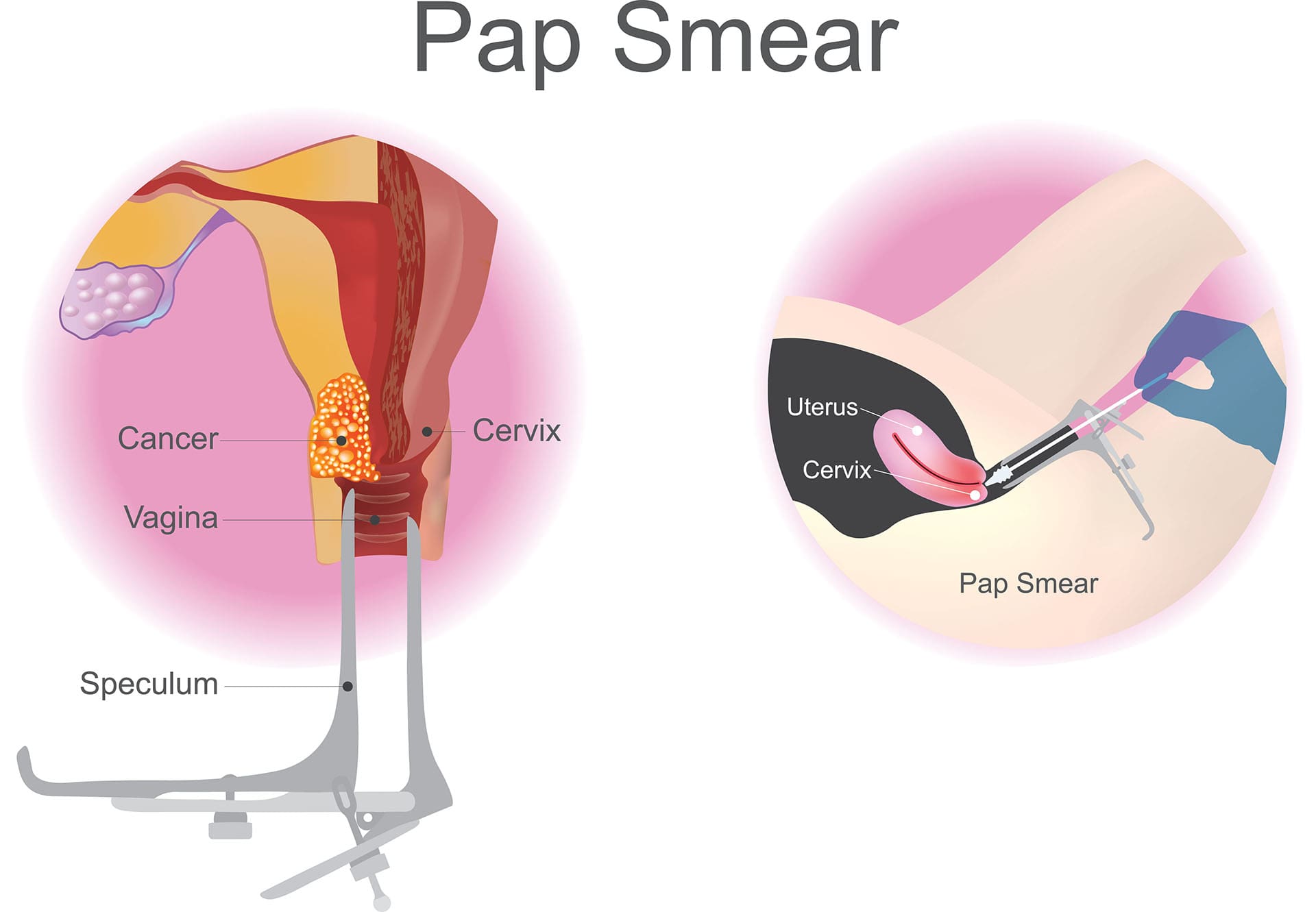
Colposcopy is a procedure undertaken after abnormal cells are found during cervical screening. A colposcope is used to examine the cervix's lower part of the womb.
One predominant type of cancer - cervical cancer develops from the abnormal cells in the cervix. These cells are not always harmful and can go away on their own, but in some cases, they develop into cancer of the cervix if they are not treated. At Medical Express Clinic, consultant gynaecologists provide abnormal smear tests and colposcopy examinations for women and recommend the right treatment for you.
Being asked to carry out a colposcopy doesn’t mean that you have cancer. It’s unlikely for abnormal cells to develop into cancer while waiting to get a colposcopy done. A colposcopy is always done after a cervical screening. Your doctor will refer you within a few weeks after your cervical screening if any of the following happens.
It is also possible to do a colposcopy examination to find out the cause of bleeding after sex or any other unusual vaginal bleeding.
If you have been asked to carry out a colposcopy, there are certain things you need to avoid for at least 24 hours before your colposcopy examination to avoid a wrong result. This includes:
It would be best to have sanitary towels handy because there may be slight bleeding or discharge after the procedure. You wouldn’t have to worry about avoiding certain types of food. Before a colposcopy, there are no eating restrictions, so you can eat whatever you want.
You need to be comfortable during your colposcopy so that you can contact your nearest colposcopy clinic in London before your appointment if:
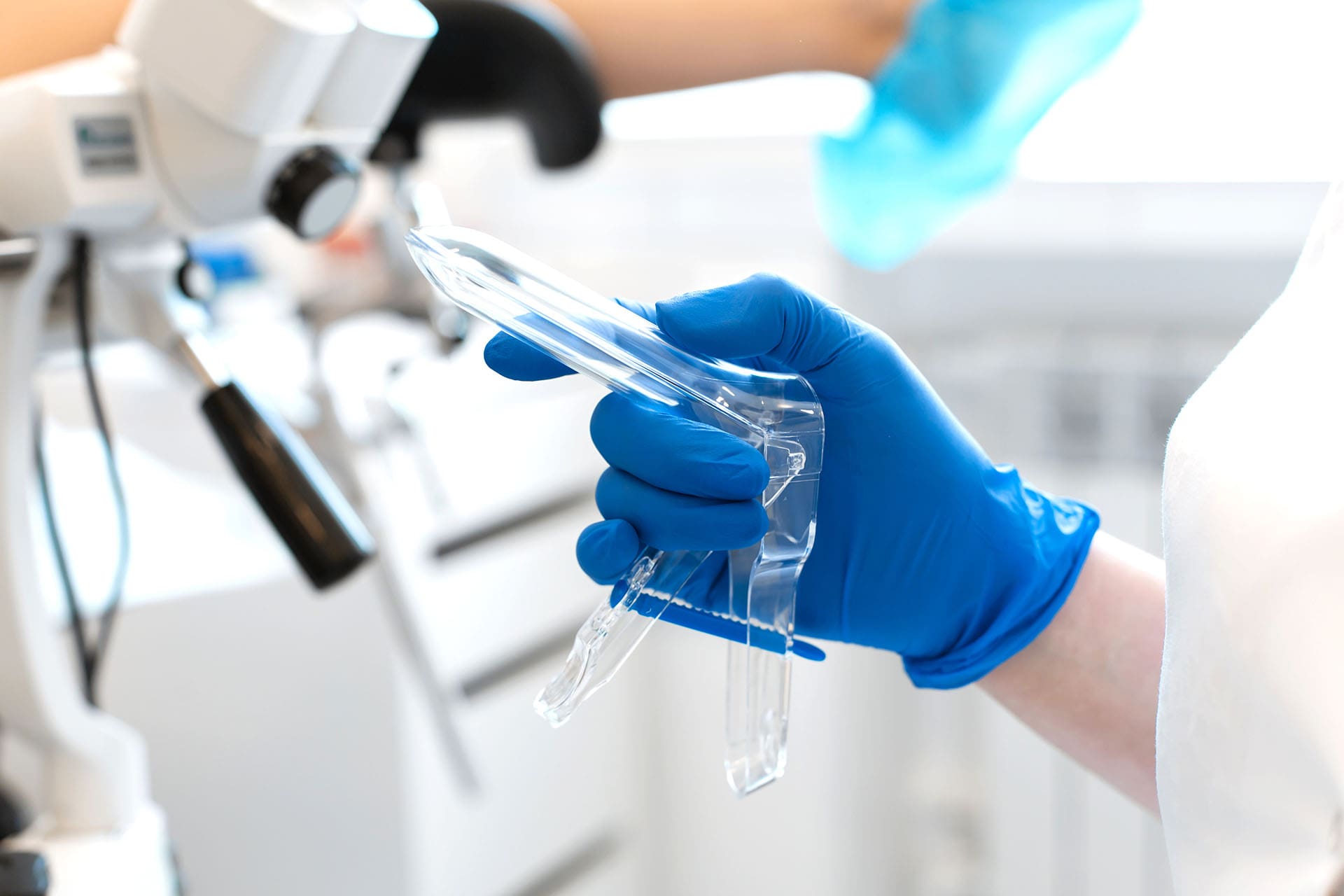
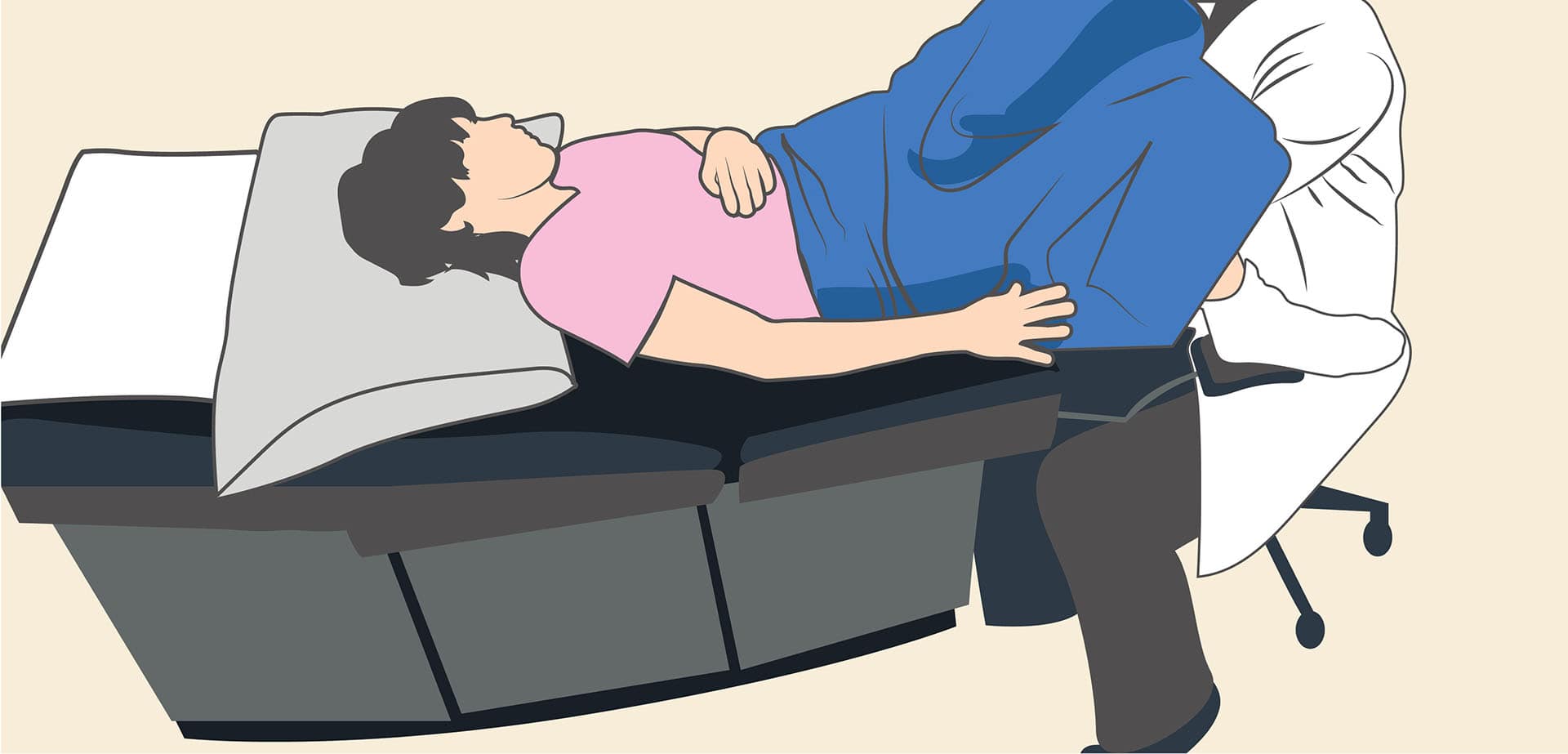
The colposcopy is done in a clinic. The procedure lasts for 15 – 20 minutes, and you will be free to go home and get on with your normal activities.
In the private clinic, a Gynaecologist carries out the colposcopy procedure. During the procedure:
Suppose the abnormal cells in your cervix are obvious during the colposcopy test. In that case, you may be offered immediate treatment to remove the cells or wait until your biopsy result is ready.
Live life to the fullest with our range of Consultant-led Gynaecological services.
BOOK ONLINE NOWit's easier, quicker and only takes 30 sec
After a colposcopy:
Colposcopy is usually a safe procedure and it doesn't lead to any severe complications; however, some women may experience some of the following side effects:
All these side effects should not be severe or last for long. If your bleeding is heavier than your normal period or the discharge is smelly or if you have severe stomach pain, you should contact your nearest clinic immediately.
In most cases, the doctor will provide the result of the procedure right away, but when a biopsy is done, the results may take about 4 - 8 weeks.
The result may either be normal or abnormal.
It means that there were no abnormal cells in the tissue sample taken from the cervix and no treatment is required.
It is important to continue with cervical screening if the abnormal cells become apparent in the future. The screening will be scheduled for 3 – 5 years depending on the woman’s age. This outcome is usually found in about 4 in every 10 women who get the procedure done.
It means that cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical glandular intraepithelial neoplasia (CGIN) cells were found in the cervix. This doesn't mean that you have cervical cancer, but there is a risk of developing this cancer if the cells are not treated. This result is usually seen in about 6 in every 10 women.
These abnormal cells are mostly determined during the colposcopy procedure, but a biopsy is needed to determine the risk of these cells becoming cancerous. The number used after the cell name determines the chances of the cells developing into cancer cells. A higher number means there is a higher risk of becoming cancerous.
A biopsy can show any of these results.
There are times that colposcopy and biopsy may find cancerous cells outright, but this happens rarely.
The next thing that is done after discovering a high-risk abnormal cell is treatment. The purpose of treatment is to remove abnormal cells while causing minimal damage to healthy cells. The abnormal cells are usually the size of the fingertip.
Sometimes treatment is done alongside the colposcopy procedure, especially when a biopsy is not required. There are certain times when you will have to wait for your biopsy result before you can undergo any of the following types of treatment.
Loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) is one of the most common treatments for abnormal cervical cells. It is also called a loop biopsy, loop excision, loop cone, or diathermy. It can be done while carrying out a colposcopy, but a local anaesthetic is needed to numb the cervix before the treatment. Going home after the treatment is possible - an overnight stay is not necessary.
LLETZ involves using a thin wire loop heated with an electric current to remove the abnormal cells.
This option of treatment is not as common as LLETZ. It is used when a large area of the cervix is affected and needs a general aesthetic to be carried out.
This treatment is usually carried out when you are asleep. It is a minor operation involving making a cone-shaped incision on the cervical tissue containing abnormal cells to remove them. In some cases, you might request to stay overnight at the clinic.
Other common treatments include:
After treatment, you can go home to rest or stay overnight at the clinic. You may be advised to:
You will not need to be screened for another three years if neither HPV nor abnormal cells are found.
There are a few risks associated with the treatment of abnormal cells, but they are nothing compared to its benefits. These risks include:
Some other serious complications may arise:
If you want to schedule your consultation or have any questions about the colposcopy cost and test, please call our doctors at 02074991991 or book an appointment online.